This post may contain affiliate links which means I may receive a commission for purchases made through links. Learn more on my Private Policy page.
Introduction: Keto Versus Paleo Defined
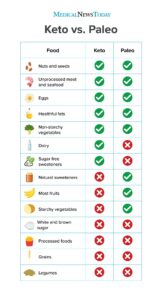 The ketogenic (keto) and Paleolithic (paleo) diets have gained considerable attention in recent years due to their touted health benefits and potential for weight loss. While both focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, there are key differences between them. In this in-depth analysis, we will explore the similarities and differences between these two popular diets, their potential benefits, and considerations to make an informed choice.
The ketogenic (keto) and Paleolithic (paleo) diets have gained considerable attention in recent years due to their touted health benefits and potential for weight loss. While both focus on consuming whole, unprocessed foods, there are key differences between them. In this in-depth analysis, we will explore the similarities and differences between these two popular diets, their potential benefits, and considerations to make an informed choice.
The Ketogenic Diet: Low Carb, High Fat
The ketogenic diet is a low-carbohydrate, high-fat, and moderate-protein diet designed to shift the body’s metabolism from burning glucose to burning fat for fuel. This metabolic state, known as ketosis, occurs when the liver converts fatty acids into ketone bodies, which are then used as the primary energy source. The keto diet typically consists of the following macronutrient ratios:
- 70-80% fat
- 20-25% protein
- 5-10% carbohydrates
The Paleolithic Diet: Ancestral Eating Principles
The Paleolithic diet, often referred to as the “caveman diet,” aims to replicate the dietary habits of our hunter-gatherer ancestors. The main premise of this diet is that our genetics have not significantly evolved since the Paleolithic era and that consuming foods available during that time can optimize health. The paleo diet primarily focuses on:
- Lean meats
- Fish and seafood
- Fruits
- Vegetables
- Nuts and seeds
- Healthy fats
Key Differences Between Keto Versus Paleo
While both diets prioritize whole, unprocessed foods and share some similarities, there are several key differences between the keto and paleo diets.
- Carbohydrate Intake: The keto diet strictly limits carbohydrate intake to 5-10% of total calories, while the paleo diet permits a more flexible range of carbohydrates from fruits and vegetables.
- Fat Sources: The keto diet emphasizes saturated and monounsaturated fats, whereas the paleo diet promotes a balance of omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids from sources like fish, nuts, and seeds.
- Dairy Products: The keto diet allows dairy products, such as cheese, butter, and cream, while the paleo diet excludes them due to their association with the agricultural revolution.
- Legumes and Grains: Both diets exclude grains; however, the paleo diet also eliminates legumes, while the keto diet permits them in moderation.
Benefits of the Ketogenic Diet – Keto Versus Paleo
The ketogenic diet has been associated with various health benefits, including:
- Weight Loss: The keto diet can promote rapid weight loss due to its ability to suppress appetite and increase fat-burning efficiency.
- Improved Blood Sugar Control: The low carbohydrate intake can help regulate blood sugar levels, potentially benefiting individuals with type 2 diabetes or insulin resistance.
- Enhanced Mental Clarity: Many keto dieters report increased mental clarity and focus, likely due to the brain’s utilization of ketone bodies for fuel.
- Reduced Inflammation: Ketone bodies have anti-inflammatory properties, which can be beneficial for individuals with chronic inflammatory conditions.
Benefits of the Paleolithic Diet
The Paleolithic diet also offers numerous health benefits, including:
- Weight Loss: The focus on whole, unprocessed foods and elimination of refined carbohydrates can promote weight loss and help prevent weight regain.
- Improved Digestion: By eliminating processed foods and emphasizing natural, fiber-rich options, the paleo diet can promote a healthy gut microbiome and improved digestion.
- Reduced Inflammation: The emphasis on omega-3 fatty acids and antioxidant-rich fruits and vegetables can help reduce inflammation in the body. 4. Heart Health: The paleo diet’s focus on lean meats, healthy fats, and nutrient-dense plant-based foods can contribute to improved cardiovascular health.Choosing the Right Diet for You: Factors to ConsiderWhen deciding between the Keto Versus Paleo, it is essential to consider individual preferences, health goals, and lifestyle factors. Here are a few key aspects to evaluate when making your choice:
- Weight Loss Goals: If rapid weight loss is your primary objective, the ketogenic diet may provide quicker results. However, the paleo diet can also promote sustainable weight loss over time.
- Health Conditions: Individuals with type 2 diabetes, insulin resistance, or neurological conditions may benefit more from the keto diet due to its impact on blood sugar control and anti-inflammatory effects. Conversely, those with a history of cardiovascular disease or high cholesterol may prefer the paleo diet’s balanced approach to fats and nutrient-rich foods.
- Sustainability: The ketogenic diet’s strict carbohydrate restrictions may be challenging for some individuals to maintain long-term. The paleo diet’s more flexible approach to carbohydrates and broader range of food options may be more sustainable for many people.
- Personal Preferences: It is crucial to consider personal taste preferences and dietary habits when choosing between these two diets. Some individuals may find the high-fat, low-carb approach of the keto diet more appealing, while others may prefer the whole-food focus and varied options of the paleo diet.
Conclusion: Keto and Paleo Diets Offer Unique Benefits
Ultimately, both the ketogenic and Paleolithic diets offer distinct health benefits and potential for weight loss. The keto diet‘s low-carb, high-fat approach may be more suitable for those seeking rapid weight loss and improved blood sugar control, while the paleo diet’s emphasis on nutrient-dense, whole foods may better align with the goals of individuals focused on long-term health and sustainability. It is essential to consider personal preferences, health goals, and lifestyle factors when deciding which diet is the best fit for you.
More info here https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/paleo-vs-keto
